Introduction
The ASTM B211M standard is a critical specification that governs the production and quality assurance of aluminum and aluminum-alloy bar, rod, and wire in metric units. This standard is widely used in various industries, including aerospace, construction, and manufacturing, to ensure that aluminum products meet stringent quality and performance criteria. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the ASTM B211M standard, its key sections, and its importance in the aluminum industry.
Overview and Scope
ASTM B211M covers rolled or cold-finished bar, rod, and wire in various aluminum alloys and tempers. The standard specifies the chemical composition, mechanical properties, heat treatment, and quality assurance requirements for these products. It is the metric counterpart of ASTM B211, facilitating global applicability and consistency. The standard is issued under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B07 on Light Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B07.03 on Aluminum Alloy Wrought Products.
ASTM B211M Mind Map:
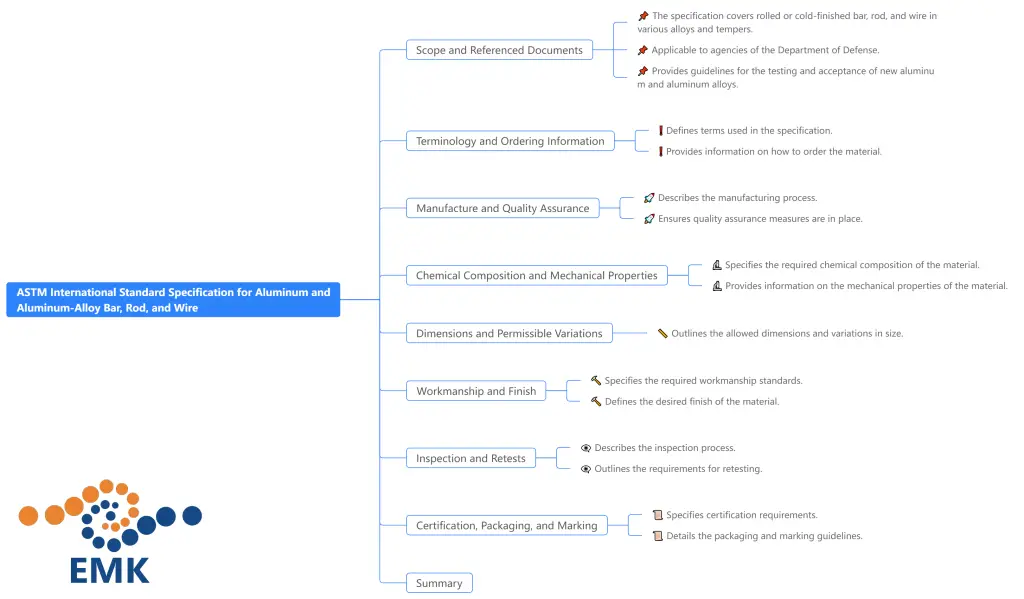
Key Sections of ASTM B211M
- Referenced Documents:
- The standard references several other ASTM standards and practices, ensuring comprehensive coverage of all aspects of aluminum product manufacturing and testing. Key references include:
- ASTM B660: Practices for Packaging/Packing of Aluminum and Magnesium Products.
- ASTM B666/B666M: Practice for Identification Marking of Aluminum and Magnesium Products.
- ASTM B918: Practice for Heat Treatment of Wrought Aluminum Alloys.
- ASTM B557M: Test Methods for Tension Testing Wrought and Cast Aluminum- and Magnesium-Alloy Products.
- ANSI H35.1M: Alloy and Temper Designation Systems for Aluminum.
- ANSI H35.2M: Dimensional Tolerances for Aluminum Mill Products.
- The standard references several other ASTM standards and practices, ensuring comprehensive coverage of all aspects of aluminum product manufacturing and testing. Key references include:
- Chemical Composition:
- Table 1 of ASTM B211M specifies the chemical composition limits for various aluminum alloys. These limits ensure that the material meets the required purity and alloying element specifications. For example, Alloy 6061 must contain 0.40-0.8% Silicon, 0.7% Iron, 0.15-0.40% Copper, 0.15% Manganese, 0.8-1.2% Magnesium, 0.04-0.35% Chromium, 0.25% Zinc, and the remainder being Aluminum. The chemical composition is critical for determining the material’s properties and suitability for specific applications.
- Mechanical Properties:
- Table 2 outlines the tensile properties, including tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation for different alloys and tempers. These properties are critical for determining the suitability of the material for specific applications. For instance, Alloy 6061 in T6 temper must have a minimum tensile strength of 290 MPa and a minimum yield strength of 240 MPa. The mechanical properties ensure that the material can withstand the required loads and stresses in its intended application.
- Heat Treatment:
- The standard specifies the heat treatment processes for different tempers, ensuring that the material achieves the desired mechanical properties. Heat treatment practices are detailed in AMS 2772 and ASTM B918. For example, Alloy 7075 in T6 temper must undergo solution heat treatment followed by aging to achieve the specified mechanical properties. Heat treatment is a critical process that affects the material’s microstructure and properties.
- Quality Assurance:
- The producer is responsible for performing all inspection and test requirements unless otherwise specified in the contract. The standard defines lot sizes for inspection and the number of samples required for testing. For heat-treated tempers, an inspection lot consists of an identifiable quantity of material traceable to a heat-treat lot or lots. Quality assurance ensures that the material meets the specified requirements and is free from defects.
- Dimensional Tolerances:
- Variations from specified dimensions are not to exceed the permissible variations outlined in ANSI H35.2M. This ensures that the material meets the required dimensional accuracy. For example, the diameter tolerance for round rod and wire is specified in Table 9.1 of ANSI H35.2M. Dimensional tolerances are critical for ensuring that the material fits and functions correctly in its intended application.
- Identification and Marking:
- When specified, materials must be marked according to ASTM B666/B666M. This includes marking for identification and traceability, which is crucial for quality control and certification. For instance, 2000 and 7000 series alloys furnished in the T6, T651, T73, T7351, or T851 tempers must be marked with the lot number. Identification and marking ensure that the material can be traced back to its production batch and verified for quality.
- Packaging and Shipping:
- The material must be packaged to provide adequate protection during handling and transportation. Packaging requirements are detailed in ASTM B660, ensuring safe delivery to the end user. Each package must contain only one size, alloy, and temper of material unless otherwise agreed. Proper packaging and shipping ensure that the material arrives at its destination in good condition.
Detailed Exploration of Key Sections
Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of aluminum alloys is a critical factor that determines their properties and suitability for various applications. The ASTM B211M standard specifies the chemical composition limits for a wide range of aluminum alloys. These limits ensure that the material meets the required purity and alloying element specifications.
For example, Alloy 6061, one of the most commonly used aluminum alloys, must contain:
- 0.40-0.8% Silicon
- 0.7% Iron
- 0.15-0.40% Copper
- 0.15% Manganese
- 0.8-1.2% Magnesium
- 0.04-0.35% Chromium
- 0.25% Zinc
- The remainder being Aluminum
The chemical composition is determined using suitable chemical or spectrochemical methods, such as those outlined in ASTM E34, E607, and E1251. These methods ensure accurate determination of the alloying elements and impurities.
Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of aluminum alloys, including tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation, are critical for determining their suitability for specific applications. The ASTM B211M standard specifies the mechanical properties for various alloys and tempers in Table 2.
For instance, Alloy 6061 in T6 temper must have:
- A minimum tensile strength of 290 MPa
- A minimum yield strength of 240 MPa
- A minimum elongation of 10%
These properties are determined using tension tests conducted in accordance with ASTM B557M. The tests involve applying a uniaxial load to a specimen until it fractures, and measuring the resulting stress and strain. The mechanical properties ensure that the material can withstand the required loads and stresses in its intended application.
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is a critical process that affects the microstructure and properties of aluminum alloys. The ASTM B211M standard specifies the heat treatment processes for different tempers, ensuring that the material achieves the desired mechanical properties.
For example, Alloy 7075 in T6 temper must undergo:
- Solution heat treatment at a temperature of 465-480°C
- Quenching in water
- Aging at a temperature of 120°C for 24 hours
The heat treatment practices are detailed in AMS 2772 and ASTM B918. These practices ensure that the material achieves the required mechanical properties and is free from defects such as porosity and segregation.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the ASTM B211M standard. The producer is responsible for performing all inspection and test requirements unless otherwise specified in the contract. The standard defines lot sizes for inspection and the number of samples required for testing.
For heat-treated tempers, an inspection lot consists of an identifiable quantity of material traceable to a heat-treat lot or lots. For nonheat-treated tempers, an inspection lot consists of an identifiable quantity of material subjected to inspection at one time.
The quality assurance process involves:
- Sampling and testing the material to ensure it meets the specified requirements
- Inspecting the material for defects such as cracks, inclusions, and porosity
- Verifying the chemical composition and mechanical properties
Quality assurance ensures that the material meets the specified requirements and is free from defects.
Dimensional Tolerances
Dimensional tolerances are critical for ensuring that the material fits and functions correctly in its intended application. The ASTM B211M standard specifies the permissible variations from specified dimensions in ANSI H35.2M.
For example, the diameter tolerance for round rod and wire is specified in Table 9.1 of ANSI H35.2M. The tolerances ensure that the material meets the required dimensional accuracy and can be used in precision applications.
Identification and Marking
Identification and marking are crucial for quality control and certification. The ASTM B211M standard specifies that materials must be marked according to ASTM B666/B666M. This includes marking for identification and traceability.
For instance, 2000 and 7000 series alloys furnished in the T6, T651, T73, T7351, or T851 tempers must be marked with the lot number. Identification and marking ensure that the material can be traced back to its production batch and verified for quality.
Packaging and Shipping
Proper packaging and shipping are essential for ensuring that the material arrives at its destination in good condition. The ASTM B211M standard specifies the packaging requirements in ASTM B660.
The material must be packaged to provide adequate protection during handling and transportation. Each package must contain only one size, alloy, and temper of material unless otherwise agreed. Proper packaging and shipping ensure that the material arrives at its destination in good condition.
Importance of ASTM B211M
The ASTM B211M standard is essential for maintaining the quality and performance of aluminum products. By adhering to this standard, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet the stringent requirements necessary for critical applications. This standard also facilitates international trade by providing a common framework for specifying and testing aluminum products.
Industry Applications
The ASTM B211M standard is widely used in various industries, including aerospace, construction, and manufacturing. The following sections explore the applications of the standard in these industries.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry relies heavily on aluminum alloys for their high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and excellent machinability. The ASTM B211M standard ensures that aluminum products used in aerospace applications meet the stringent quality and performance requirements.
For example, Alloy 7075 is commonly used in aerospace applications due to its high strength and excellent fatigue resistance. The T6 temper of Alloy 7075 is used in aircraft structures, such as wings and fuselage frames, where high strength and low weight are critical.
The heat treatment and quality assurance requirements specified in ASTM B211M ensure that the material meets the required mechanical properties and is free from defects. This is critical for ensuring the safety and reliability of aerospace components.
Construction Industry
The construction industry uses aluminum alloys for their lightweight, corrosion resistance, and ease of fabrication. The ASTM B211M standard ensures that aluminum products used in construction applications meet the required quality and performance standards.
For example, Alloy 6061 is commonly used in construction applications due to its good mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. The T6 temper of Alloy 6061 is used in structural components, such as beams and columns, where high strength and durability are required.
The chemical composition and mechanical properties specified in ASTM B211M ensure that the material meets the required performance standards. This is critical for ensuring the safety and durability of construction components.
Manufacturing Industry
The manufacturing industry uses aluminum alloys for their excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and good mechanical properties. The ASTM B211M standard ensures that aluminum products used in manufacturing applications meet the required quality and performance standards.
For example, Alloy 2011 is commonly used in manufacturing applications due to its excellent machinability. The T3 temper of Alloy 2011 is used in precision components, such as gears and shafts, where high machinability and good mechanical properties are required.
The heat treatment and quality assurance requirements specified in ASTM B211M ensure that the material meets the required mechanical properties and is free from defects. This is critical for ensuring the quality and performance of manufacturing components.
Official ASTM B211M eBook Reference:
PDF eBook of “ASTM B211M: Standard Specification for Aluminum and Aluminum-Alloy Bar, Rod, and Wire (Metric) ”:
Conclusion
ASTM B211M is a vital standard for the aluminum industry, providing detailed specifications for the chemical composition, mechanical properties, heat treatment, and quality assurance of aluminum bar, rod, and wire. Understanding and adhering to this standard ensures that aluminum products are reliable, high-quality, and suitable for their intended applications. By following the guidelines set forth in ASTM B211M, manufacturers can produce aluminum products that meet the highest standards of quality and performance, ensuring their suitability for critical applications in various industries.
For more detailed information, refer to the full ASTM B211M document available through ASTM International and other reputable sources.

Contact us today to discuss your specific production requirements and learn more about how Elka Mehr Kimiya’s Aluminum Rods can elevate your steelmaking process.
Whatsapp Number:
+98-902-8000013
Sale Department Contact Number:
+98(41)36589245

















No comment